The sexual health of millions of men worldwide is in a precarious situation due to erectile dysfunction (ED), which is no longer a silent problem. There is little indication that this concerning trend will abate, with estimates suggesting that 322 million men worldwide may soon be impacted. This alarming figure emphasizes how urgent it is to address this problem.
The persistent inability to achieve or sustain the erection necessary for satisfying one’s sexual needs is linked to ED. Read this article as we have covered every aspect of ED, including symptoms, causes, treatments, and self-care. We have also provided answers to a few frequently asked topics, such as whether diabetes can cause erectile dysfunction and how to prevent erectile dysfunction.
There are many types of ED which depend upon the individual conditions.
Types of Erectile Dysfunction
Healthcare providers classify ED in the following categories:
- Vascular ED: It is the most common type of ED. It involves issues with blood vessels or valves (which hold blood inside the male reproductive part) in the penis, affecting the blood flow needed to achieve and maintain an erection.
- Neurogenic ED: It results from nerve issues interrupting signals from the brain reaching the penis.
Causes may include:
- Trauma
- Pelvic surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Stroke, spinal stenosis
- Multiple sclerosis (MS).
- Hormonal ED: It is majorly caused by testosterone deficiency or thyroid issues.
- The International Society for Sexual Medicine states that both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause ED due to fatigue, low mood, and low sex drive.
- Age-related testosterone deficiency is the most common cause of low testosterone, leading to ED in men.
- Psychogenic ED: It is caused by psychological conditions affecting thoughts, feelings, or behavior.
The most common symptoms of erectile dysfunction are trouble getting an erection and difficulty maintaining it during sexual activities.
Symptoms and Signs of Erectile Dysfunction
Following are the Other sexual disorders related to ED include:
- Premature ejaculation (PE)
- Needing excessive stimulation to maintain an erection
- Anorgasmia, or the inability to experience an orgasm despite sufficient stimulation
- Inconsistent erections
- Delayed ejaculation
- Erections not lasting long enough for sex
- Inability to get an erection at any time
Speak with your doctor if you have these symptoms for 3+ months to determine if an underlying condition requires treatment.
Various factors affecting your vascular, nervous, and endocrine systems can cause or contribute to ED.
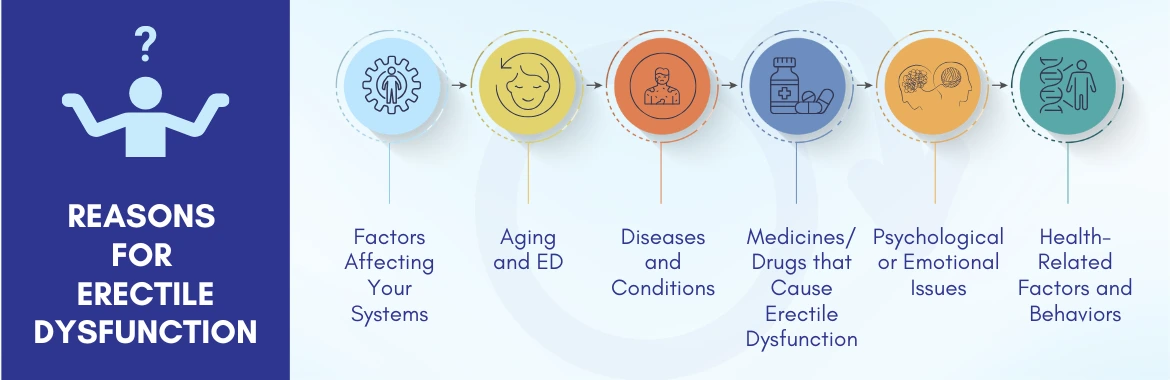
Erectile Dysfunction Causes / Reasons for Erectile Dysfunction
There are a plethora of reasons for erectile dysfunction, some of them can be the following illnesses and ailments:
-
Factors Affecting Your Systems
Many factors affecting your vascular, nervous, and endocrine systems can cause or contribute to ED.
While aging increases the likelihood of ED, it does not cause it. ED can be treated at any age.
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Peyronie’s disease
- Heart and blood vessel disease
- Atherosclerosis
- Injuries from prostate cancer treatments (radiation therapy and surgery)
- Injuries to the penis, spinal cord, prostate, bladder, or pelvis
- Surgery for bladder cancer
ED is 2-3 times more common in men with diabetes.
Medicines/Drugs that Cause Erectile Dysfunction
- Blood pressure medicines
- Tranquilizers or prescription sedatives
- Appetite suppressants
- Ulcer medicines
- Antiandrogens (used for prostate cancer therapy)
- Antidepressants
Psychological or Emotional Issues
Psychological or emotional factors that may worsen ED include:
- Smoking
- Being overweight
- Lack of physical activity
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Illegal drug use
Erectile Dysfunction Diagnosis
One of the first steps a doctor will take to assist in the diagnosis of ED is to obtain a medical and sexual history. Other diagnostic criteria are as follows:
Medical and Sexual History
- Assessing confidence in getting and maintaining erections
- Frequency and satisfaction of erections during sexual stimulation
- Morning erections and sexual desire evaluation
- Ability to climax and any contributing medications or substances
Mental Health and Physical Exam
- Psychological assessment for emotional factors
- Physical examination including penile sensitivity and appearance
- Checking for hormonal issues and circulatory problems
Lab Tests
- Blood tests to identify underlying conditions like diabetes or hormonal imbalances
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Penile Doppler ultrasound
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
- Thyroid tests
- Testosterone test
- Penile biothesiometry tests determine whether the nerves in your penis react to vibrations.
Imaging Tests
- Doppler ultrasound to measure penile blood flow and detect abnormalities
- Injection tests to assess erectile function under controlled conditions
Other Tests
- Nocturnal erection test to monitor erections during sleep
- Injection test to induce erection and evaluate response
 Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
When dealing with erectile dysfunction (ED), your doctor will first check if any existing health issues might be causing or worsening the problem. The therapy options you have will be based on what’s causing your ED and how severe it is, along with any other health conditions you might have. Your doctor will explain the risk-benefit ratios of each treatment and will consider what you and your partner prefer.
It’s important to talk with your partner about which treatment feels right for both of you, as choosing an ED treatment is a very personal decision.
Below are the treatment options available:
Lifestyle Changes
- Inculcating positive lifestyle changes can remarkably help with erectile dysfunction.
- Quitting smoking is crucial as it improves blood circulation, which is vital for erections.
- Limiting or stopping alcohol consumption can also make a difference since excessive drinking can interfere with your ability to get and maintain an erection.
- More movement in the form of physical activity, especially strength/resistance training, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential steps, too; regular exercise boosts your overall health and can improve ED.
- If you use illegal drugs, stopping is vital because they can cause or worsen ED.
- Do not be afraid to ask for assistance from a competent professional if you are having trouble implementing these changes on your own. They can offer you specific guidance and tools to help you along the way.
Psychological Counseling
If psychological or emotional issues are contributing to your erectile dysfunction, consider going to counseling. A counselor can help you address and reduce anxiety or stress related to sex, which can be a significant factor in ED. Bringing your partner to counseling sessions can also be beneficial, as it provides support and helps both of you understand and manage the situation together.
Medicines
Your doctor may change the medication you’re taking or change the dosage if it’s making your ED worse. Never discontinue taking any medicine without first talking to your physician.
Oral Medications
Oral medications are a successful treatment for many men with ED. These include:
These medications boost nitric oxide, a naturally occurring chemical that relaxes penile muscles and increases blood flow to aid in an erection in response to sexual stimulation.
Note: They are not aphrodisiacs and will not cause excitement or be needed for those with normal erections. These work when you are naturally aroused.
Other Medications
Below are the other alternative medications:
-
Alprostadil Self-Injection:
It is a self-injection in which the base or side of the penis is injected with alprostadil (Caverject, Edex) using a tiny needle. Sometimes, this method includes medications used for other conditions, combined as bimix (composed of two medications) or trimix (composed of three medications).
Each injection is designed to create an erection lasting no longer than an hour. While generally effective, side effects can include mild bleeding at the site of injection, a prolonged erection (i.e. priapism), and rarely, the formation of fibrous tissue.
When effective, an erection normally lasts between 30 and 60 minutes and starts within 10 minutes. A burning feeling in the penis, slight urethral bleeding, and the development of fibrous tissue inside the penis are possible adverse effects.
In those with low testosterone, this method may help to alleviate ED symptoms by bringing testosterone levels back to normal ranges.
-
Vacuum device/Penis pumps
A penile pump, sometimes known as a vacuum erection device, is a device that draws blood into the penis using suction to aid in erection formation. You place a hollow tube over your penis and pump out the air, which pulls blood in and causes it to swell and become erect. To maintain the erection, you slide a tension ring over the base of your penis, which keeps the blood trapped inside. After intercourse, you remove the ring.
Possible side effects include bruising, a cool feeling in the penis, and difficulty ejaculating with the ring in place. Your doctor can recommend a specific model that suits your needs and is made by a trusted manufacturer if a penis pump is a suitable option for you.
5.1 Artery reconstruction: Artery reconstruction surgery restores blood flow to the penis by repairing blocked arteries, reversing ED.
Note: It’s most effective for men under 30 with this issue.
5.2 Penile implants: Penile implants involve surgically placing devices into the sides of the penis—either inflatable or malleable rods.
- Inflatable implants let you control erection timing
- Malleable rods keep the penis firm yet flexible.
Note: These implants/surgeries are typically considered after trying other methods. Surgery carries risks like an infection. If you have a urinary tract infection, penile implant surgery isn’t advised. If you have a urinary tract infection, penile implant surgery isn’t advised.
-
Erectile Dysfunction Cream
Erectile dysfunction cream/erection creams offer a topical treatment option for ED, applied directly to the penis before sexual activity. They are considered to potentially cause fewer systemic side effects, which is beneficial for individuals with conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
Research on the efficacy and safety of ED creams is still limited, and none are currently FDA-approved. Some studies suggest promise, particularly those involving alprostadil, a natural prostaglandin found in creams like Vitaros. A 2016 review highlighted alprostadil cream as a well-tolerated and effective alternative for ED treatment. However, further clinical trials are needed, especially for populations with multiple comorbidities and nonvascular forms of ED.
Best Medicine for Erectile Dysfunction Without Side Effects
While no medication is entirely free of side effects, according to the Boston University School of Sexual Medicine, vardenafil shares structural similarities with sildenafil, whereas tadalafil is distinctly different. With a biochemical potency about ten times greater than that of sildenafil, vardenafil can produce a penile erection at lower dosages, potentially reducing side effects.
What is the latest Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction?
Existing drugs are in demand and not always effective; ongoing research focuses on long-term ED cures like regenerative therapies.
The following are the regenerative therapies:
Stem cell-based therapies, platelet-rich plasma, and gene transfer therapies:
- Aimed to provide a long-lasting cure for erectile dysfunction (ED) by addressing underlying causes rather than just providing symptomatic relief.
- Studies indicate that stem cells primarily exert their effects through paracrine mechanisms, releasing factors that aid tissue repair rather than directly differentiating into penile tissues.
- Recent research explores combining stem cells with angiogenic and neurotrophic factors to enhance therapeutic efficacy, showing promising results in animal models.
- Clinical trials in humans are limited but show potential benefits in improving penile vascular flow and erectile function scores without serious adverse effects.
- Gene transfer techniques, such as inserting the “Maxi-K” potassium channel gene into penile smooth muscle cells, have also shown some efficacy in improving erectile function in animal models and limited human studies.
Low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapies:
- Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy (LI-ESWT) uses gentle acoustic waves, similar to what’s used to break up kidney stones.
- It was first tested for erectile dysfunction (ED) in 2010 after proving effective for improving blood flow in other tissues.
- Studies suggest it can improve erectile function long-term, measured by how well you perform sexually and how hard your erections are.
- LI-ESWT works by promoting new blood vessel growth, helping tissues and nerves heal, and reducing inflammation.
- Results vary depending on how severe the ED is—more severe cases might not respond as well.
- To become a standard treatment, more research is needed to set clear rules on how intense, how often, and for how long the therapy should be used.
Intracavernous injection of botulinum neurotoxin A:
- It’s a new nonsurgical treatment where botulinum neurotoxin A is injected into the penis.
- Can induce erections when injected alone or with a PD5 inhibitor (like sildenafil).
- Effective for patients with ED who haven’t responded to other treatments and are being considered for penile implants.
- Effects can last over three months without reported side effects.
- Studies in patients and animals suggest it could be a promising treatment, but how exactly it works isn’t fully understood.
- Currently considered experimental and used as a last resort when other ED treatments fail.
Invasive surgical procedures:
at the level of the pelvic vascular (arterial and/or venous) bed, aimed at restoring satisfactory blood flow during penile erection and implanting nerve grafts in the pelvic area.
Note: Despite promising findings, standard protocols, optimal dosages, and specific cell types for different causes of ED still need extensive research before these therapies can become widely available.
Nonpharmacological strategies for the therapy of ED
| Strategy |
Mechanism of Action |
Preclinical Evidence |
Clinical Evidence |
| Stem cells (normal or modified) injected into cavernous areas |
Restoring erectile function involves activating cells and nerves in penile tissues. |
Yes, in rodent models of ED, including diabetes, vascular issues, nerve injuries, and aging. |
Yes, in ED patients with different causes, especially diabetes and prostatectomy. |
| Platelet-enriched plasma |
Restoring erectile function involves boosting activity in cells (endothelial and smooth muscle cells) and nerves within the penis. |
Yes, in rodent ED models, including diabetes, vascular issues, nerve injuries, and aging. |
Yes, in ED patients with various causes, especially diabetes and prostate surgery. |
| Gene transfer |
Genes inserted to relax cavernous smooth muscle tissues enhance erectile function. |
Yes, in aging rodent models and a monkey model of atherosclerotic ED. |
Yes, only early clinical data (Phase 1) are available for ED patients with various causes. |
| Intracavernous botulinum
neurotoxin A |
An erection occurs through the relaxation of cavernous smooth muscle, possibly by blocking the release of contractile mediators, although the exact mechanism is still unknown. |
Yes, in rodent models of ED, especially those involving hypertension. |
Yes, in ED, patients with various causes, particularly vascular issues, chosen for penile prosthesis implantation. |
Erectile Dysfunction Prevention Methods
There are various actions you can do to prevent ED. Making healthy lifestyle adjustments is a key component of many of these processes. As a result, they not only help to avoid ED but also to enhance general health.
- Quit Smoking
- Follow a Healthy Eating Plan
- Choose whole-grain foods, low-fat dairy, fruits, vegetables, and lean meats
- Steer clear of foods excessive in sodium and saturated fat.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Prevent or control hypertension and diabetes
- Be Physically Active
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity most days
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Get High-Quality Sleep
- Avoid Using Illegal Drugs
- Erectile dysfunction exercises
Kegel Exercises:
- Sitting Pelvic Floor Activation: Sit with feet flat and hip-width apart, activate pelvic floor muscles for three counts and release for three counts.
- Standing Pelvic Floor Activation: Stand with feet hip-width apart, activate pelvic floor muscles for three counts and release for three counts.
- Activating Pelvic Floor Muscles: Lie down with knees bent and feet flat, exhale and squeeze pelvic floor muscles for three counts, then inhale and release for three counts.
Pilates Exercises:
- Knee Fallouts: Lie down with knees bent and feet flat, exhale, engage pelvic floor muscles, and lower one knee to the floor without shifting your pelvis.
- Supine Foot Raises: Lie down with knees bent and feet flat, exhale, engage pelvic floor muscles, and lift one foot while maintaining stability in your pelvis and spine.
- Pelvic Curl: Lie down with knees bent and feet flat, exhale, engage pelvic floor muscles, tilt pelvis upward, lift buttocks, and squeeze while resting weight on shoulders.
Aerobic Exercises:
Cycling, Spin classes, Boxing, Rowing, Running, and Skipping are a few aerobic exercises that can help prevent ED if done regularly.
Physical Activity to Enhance Erectile Function: A Systematic Review of Intervention Studies
Aim of the Study: To determine how much physical activity is needed to reduce ED in men with the mentioned risk factors.
Method: Researchers reviewed studies from 2006 to 2016, following strict guidelines to ensure quality.
They focused on studies that explored physical activity as a treatment for ED related to lack of exercise, obesity, high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases.
Results:
- 10 studies met the criteria.
- These studies provided evidence on the amount of physical activity required to reduce ED in men with the relevant health issues.
Conclusion:
- Recommendation: Men should engage in supervised aerobic exercise. Men should engage in supervised aerobic exercise. Total weekly exercise should be 160 minutes, continued for 6 months.
- Outcome: This routine helps reduce erectile issues in men with ED linked to inactivity, obesity, high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome, and heart disease.
Related Alcohol and Erectile Dysfunction Statistics
A 2020 review found that 16% to 73% of chronic heavy alcohol users experience autonomic nervous system dysfunction.
- In a study aimed to investigate the prevalence of sexual dysfunction among male subjects diagnosed with alcohol dependence.
- A total of 100 male patients admitted to a deaddiction center with alcohol dependence syndrome (F10.30, ICD-10 criteria) were assessed using a sexual dysfunction checklist aligned with the Diagnostic Criteria for Research [ICD-10].
- Results indicated that 72% of participants exhibited one or more forms of sexual dysfunction, primarily premature ejaculation, low sexual desire, and erectile dysfunction.
- Notably, higher levels of alcohol consumption were identified as a significant predictor of sexual dysfunction onset.
- These findings underscore the substantial burden of sexual dysfunction in individuals with alcohol dependence, especially among heavy drinkers. Integrating regular sexual health assessments into clinical practice is imperative for recognizing and addressing these issues comprehensively.
Conclusion:
Erectile dysfunction (ED) affects millions but is treatable. Various medical and lifestyle interventions, including medications, counseling, and exercise, offer effective solutions. With proper treatment and diagnosis, ED can be managed, improving quality of life and sexual health. There is no need for undue worry; help is available.
FAQs
Q1 Can erectile dysfunction be cured?
A: In many cases, erectile dysfunction (ED) is temporary and can improve with better health habits. If there’s a medical reason, like nerve damage or poor blood flow, medication might be needed. The first step is figuring out what’s causing the ED, and a doctor can help with that. Although getting older can increase the chances of ED, it doesn’t directly cause it, and it can be treated at any age.
Q2 Can high blood pressure cause erectile dysfunction?
A: Yes, high blood pressure can cause erectile dysfunction (ED). It puts extra strain on your organs and slows down blood flow, making it harder to maintain an erection. Many men with high blood pressure experience ED as a result.
Q3 When does erectile dysfunction start?
A: Older men are more likely to experience erectile dysfunction (ED) however, it can occur at any age. About 9% of men between 40 and 44 years old experience ED, and this number goes up to 56% for men over 65. In total, around 50 million men in the U.S. have ED.
Q4 Can diabetes cause erectile dysfunction?
A: Yes, diabetes can cause erectile dysfunction (ED). About half of men with diabetes experience ED because the disease can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the penis. Men with diabetes are about 3.5 times more likely to have ED than those without diabetes.
Q5 What vitamins help with erectile dysfunction?
A: A: Vitamin D is one of the most researched vitamins for treating erectile dysfunction (ED). It’s linked to sexual function and heart health. A study from 2020 found that low vitamin D levels are associated with worse ED symptoms. Researchers think vitamin D might help ED by enhancing blood flow to the penis and maintaining the optimal production of sex hormones like testosterone, but more research is needed.
Other helpful vitamins might include:
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid)
- Vitamin B3 (niacin)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B12
Q6 How common is erectile dysfunction?
A: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is quite common. Around 52% of men between 40 and 70 experience some difficulty with erections, and 1 in 10 men have long-term issues with ED.
Dr. Bajic says that ED can affect men of any age and can happen for various reasons. It’s also important to note that ED isn’t just an all-or-nothing condition. You might still get erections, but they could be weak or short-lived.
Q7 How to know if I have erectile dysfunction?
A: You might have erectile dysfunction (ED) if you often have trouble getting or keeping an erection or if your sexual desire is reduced. It’s normal to have occasional erection issues, but if it occurs a lot, talk to your medical practitioner. They can help figure out what’s causing it and suggest treatments, which might include medication or addressing an underlying condition.
KeyFacts
Affect age group: It can happen at any age, more common as men get older
Body part involved: Corpora cavernosa in the shaft of the penis
Necessary health tests/imaging:
- Blood tests to identify underlying conditions like diabetes or hormonal imbalances
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Penile Doppler ultrasound
- Psychological assessment for emotional factors
Treatment
- Oral
- Medications (Avanafil, Sildenafil, Tadalafil, Vardenafil)
- Other Medications (Alprostadil Self-Injection, Alprostadil Urethral Suppository, Testosterone Replacement)
- Vacuum device/Penis pumps
- Recommend Surgery (Artery reconstruction, Penile implants)
- Erectile Dysfunction Cream: Alprostadil cream
- Latest Treatment: Stem cell-based therapies, platelet-rich plasma, gene transfer therapies, Intracavernous injection of botulinum neurotoxin A, and low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapies.
Specialists to consult:
- Endocrinologist
- Urologist
Did you know?
For centuries, the Zulu people of South Africa have harnessed the power of Eriosema roots to combat erectile dysfunction and impotence, blending ancient wisdom with modern health practices.











 Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
